Search Results
By content type
By section
-
Heat Exchanger Effectiveness
Calculating heat exchanger effectiveness allows engineers to predict how a given heat exchanger will perform a new job. Essentially, it helps engineers predict the stream outlet temperatures without a trial-and-error solution that would otherwise be necessary. Heat exchanger effectiveness is defined as the ratio of the actual amount of heat transferred to the maximum possible amount of heat that could be transferred with an infinite area.
Two common methods are used to calculate the effectiveness, equations and graphical. The equations are shown below:
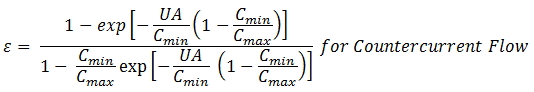
Eq. (1) 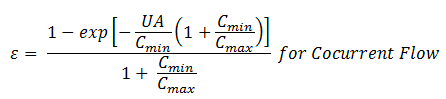
Eq. (2)
where:{parse block="google_articles"}Â
U = Overall heat transfer coefficient
A = Heat transfer area
Cmin = Lower of the two fluid's heat capacities
Cmax = Higher of the two fluid's heat capacitiesOten times, another variable is defined called the NTU (number of transfer units):
NTU = UA/CminWhen NTU is placed into the effectiveness equations and they are plotted, you can construct the plots shown below which are more often used than the equations:
Then, by calculating the Cmin/Cmax and the NTU, the effectiveness can be read from these charts. Once the effectiveness has been found, the heat load is calculated by: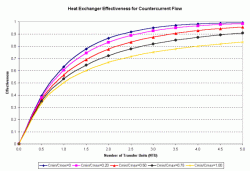
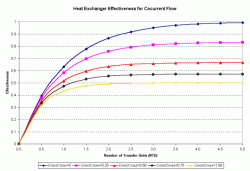
Figure 1: Heat Exchanger Effectiveness
for Countercurrent FlowFigure 2: Heat Exchanger Effectiveness
for Cocurrent FlowQ = Effectiveness x Cmin x (Hot Temperature in - Cold Temperature in)
and the outlet temperatures can be calculated by: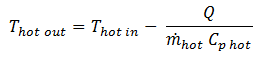
Eq. (3) 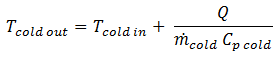
Eq. (4) - Oct 16 2012 12:15 PM
- by Chris Haslego

 FB
FB

