Gas Boots are provided upstream of a Crude Oil Dehydration tank in order to degass the crude oil before it enters the dehydration tank. Entrained gas in crude oil disturbs the settling process in a dehydration tank and it's removal is required to ensure quick and effective settling for separating bulk water in crude oil dehydration tanks also referred commonly as "Free Water Knockout" (FWKO) tanks.
It is important to note that Gas Boots are very effective up to a Gas-Oil-Ratio (GOR) of 10 Nm3/m3. Above the aforementioned GOR, a conventional gas-liquid separator is recommended.
In a gas boot the downward liquid velocity should not exceeed 0.1 m/s.
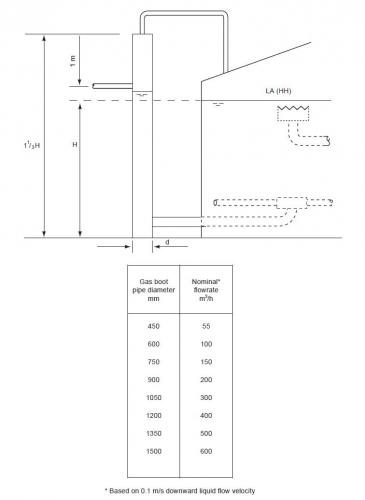
Gas boots are generally designed as a piece of piping in the inlet piping to the FWKO just uptream of the inlet connection to the FWKO. Today's blog entry provides a quick sizing method in terms of the diameter of the gas boot pipe and the wet and unstabilized crude oil nominal flow rate based on a reputed company guideline.
Refer the attachment for the sizing of gas boots.
Any comments are welcome.
Regards,
Ankur.

 FB
FB







Dear Ankur,
1. Based on the sketch you have provided, the outlet gas stream is connected to top of FWKO. Is this acceptable to let the gas to enter the top space of storage tank after getting separation from oil? Isn't it better to route it to gas outlet line from FWKO?
2. Regarding to the sizing of gas boots some clients ask to include slug volume of feed pipeline into gas boot volume. Is this part of gas boot function such that can handle any slug volume from feed line?
Thanks a lot.